Encyclopedia
Ruby Full Guide

Ruby, from the Latin rubeus meaning “red,” is one of the four traditional precious stones, alongside emerald, sapphire, and diamond. As a member of the corundum family, ruby is prized for its deep red color, brilliance, and exceptional hardness. Symbol of passion, strength, and vitality, ruby has long been considered a stone of love and power. It is the birthstone for July and the gem traditionally gifted for a 35th wedding anniversary — the ruby anniversary.
Characteristics of the ruby
Etymology: From the Latin rubeus, meaning "red stone".
Family: Corundum
Chemical composition: Aluminum Oxide/Chromium
Hardness: 9 on the Mohs scale
Density: 3.95 – 4.05
Optical properties: Negative uniaxial
Refractive index: 1.762 – 1.770
Birefringence: 0.008 – 0.010
Crystal system: Hexagonal

The origin of Rubies
The famous Mogok valley in Myanmar (formerly Burma) has for several centuries been the home of the most beautiful rubies in the world, renowned for their unique red color. These mines have now almost run dry, making the Myanmar rubies among the most sought-after stones.
Nowadays this red corundum stone mostly mined in other parts of the world, such as Mozambique, Sri Lanka, Madagascar, Malawi, Kenya, Tanzania, Thailand and even Greenland, where a new mine has been recently discovered.
Wherever they are sourced from, the large majority of rubies are cut and sold on the market in Thailand.
Carat
The carat is the standard unit of measurement for the weight of precious stones. 1 carat is equal to 0.2 gram.
But be careful not to confuse carats with karats, which is a unit used to determine the purity of gold.
As rubies are, along with the sapphires, denser than other precious stones, a 1-carat round ruby will be smaller in size than a 1-carat round diamond or 1-carat round emerald.
The color of the Ruby
The ruby is a red gemstone and its color is prized above all else, including clarity and weight, when it comes to assessing its value. This corundum stone owes its red color to the fairly high concentration of chromium in its composition. It can also vary in color depending on its origin, ranging from orange-red all the way to a purplish blue or even brownish red.
Rubies sourced from Myanmar are the most renowned and are prized for their pure red color. In fact, certain Mogok valley rubies have been dubbed 'pigeon blood' rubies for their vivid and highly saturated color that has just the slightest touch of fuchsia. These rubies are extremely rare and very expensive. This name can only officially be used for rubies from Myanmar but is often used liberally.
Rubies with a similar color and properties to the Myanmar stones can also be found in one particular mine in northern Vietnam, as well as in the Morogoro region of Tanzania.
Rubies from Central and South-East Asia tend to contain a touch of pink. Rubies from East Africa often have a slight orange hue, such as rubies from Mozambique or the Winza region of Tanzania. And Madagascan rubies are known for their purplish hue.
Discover our Guide on the Colors of Gemstones.

Pinkish ruby

Pigeon blood ruby

Brownish ruby

The clarity of Rubies
When buying a ruby, clarity is a far less important factor than color as all natural rubies contain small impurities. These impurities, which are also known as inclusions, are more or less visible to the naked eye, but there is no such thing as a perfectly 'clean' ruby, i.e. without inclusions.
However, as rubies with less visible inclusions are rarer, they are naturally more expensive.
Cut & Shapes
The ruby can be cut into a variety of different shapes, including oval, heart, pear, cushion and round due to its elevated hardness. But the most common ruby cut is the oval cut, as it involves the least amount of loss of raw material during cutting.
Industry standards dictate that gemstones must be faceted in line with certain proportions (table plane perpendicular to the main C-axis) in order to bring out the best possible hue, but perfectly cut rubies are very rare.
The culet, i.e. the bottom part of the stone, is often slightly off-center or cut more deeply than is standard to bring out the best color possible.

Emerald Cut Ruby

Oval Shape Ruby

Marquise Shape Ruby

Princess Cut Ruby

Round Shape Ruby

Pear Shape Ruby
Birthstone & Wedding Anniversary
The ruby is the birthstone of peole born in July.
It is also used to celebrate 35 years of marriage in France and 40 years of marriage in the US.
Discover our Birthstone Full Guide.
Famous Rubies
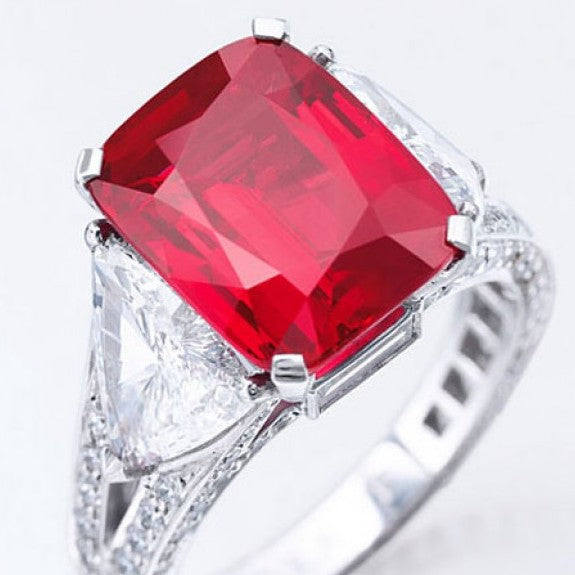

Sunrise Ruby
The Sunrise Ruby is a 25.59-carat 'pigeon blood' Myanmar ruby. It is set into a ring that was sold at Sotheby's in May 2015 for over $30 million, when it simultaneously broke the price-per-carat record for a ruby, which is over $1 million per carat.

Crimson Flame Ruby
The Crimson Flame Ruby is a magnificent 15.04-carat cushion stone from Myanmar, set in a ring with a diamond halo. It was sold at a Christies auction in December 15 for $18 million. This amounts to a record-breaking $1.2 million per carat.

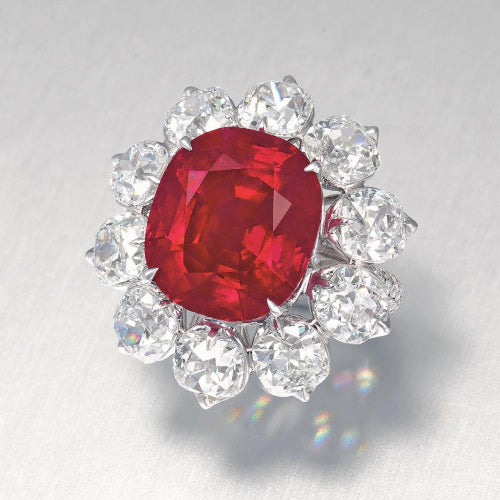
Carmen Lucia Ruby
The Carmen Lucia Ruby was discovered in the 1930s and is a 23.1-carat stone boasting exceptional clarity. It was given to the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, DC by businessman Peter Buck in remembrance of his late wife Carmen Lucia. It is widely considered to be one of the most beautiful Myanmar rubies ever found.

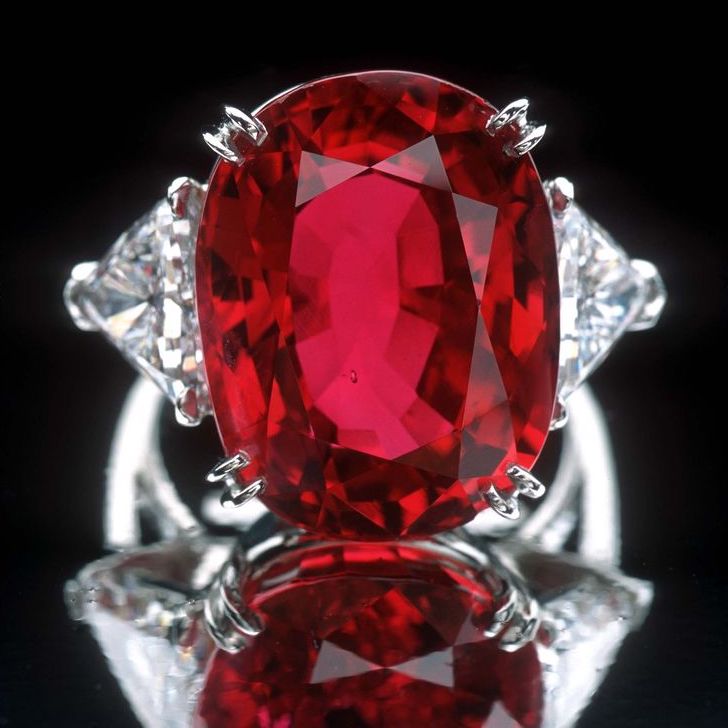
Richard Burton Ruby
The Richard Burton ruby is an exceptional 8.24-carat Myanmar ruby set into a diamond ring given to Elizabeth Taylor by Richard Burton in 1968. It was sold for $4.2 million at Christie's in 2011, which adds up to over $500,000 per carat.
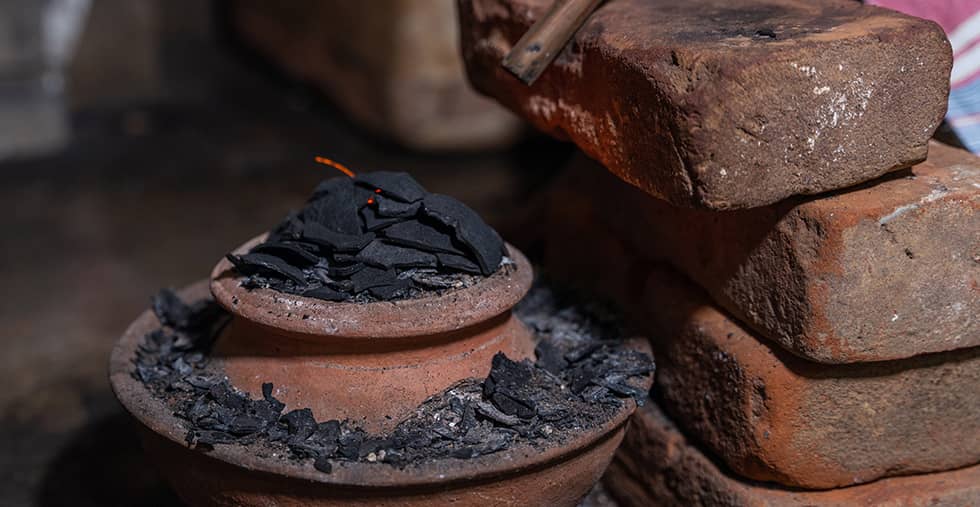

Treatment
Like sapphires, it is extremely rare to find high quality natural rubies that have not undergone treatment.
The most common method for enhancing a ruby consists of heating the stone at temperatures between 1,500 and 1,800°C so that its color intensifies and its inclusions crystallize and become less visible. This type of heat treatment, known as embellishment, is used on the majority of rubies on the market, which is why purchasing an unheated ruby is an excellent investment. However, it must have a certificate from a recognized laboratory (e.g. GIA, Gubelin, GRS, IGI, etc.).
There are other types of changes that can be made to a stone, including lead-based treatments, but these are not officially recognized by industry standards.
What Customers Are Saying
Very happy, would order again!!
Very happy with this ring for my wife. I keep coming back to Gemnat because their quality and prices are hard to beat. They are a lot more cheaper than other online websites I have checked but the quality is just the same or even better. I highly recommend them to everyone who wants a great quality of jewelry. I'm already planning my next purchase with them hihi
User-friendly website and secure checkout.
Top notch. I've ordered from Gemnat twice and the product and the service level is always flawless.
Luxury Service + Quality
This was my first time buying fine jewelry online and I had zero clue what I was doing 😅. I picked out a morganite ring and was worried about how it would look in real life. When it arrived, I was completely blown away!! The stone sparkles more than I expected, the band is perfect, and the packaging is so elegant! The team even helped me with sizing questions via chat. I’m officially hooked on Gemnat!
This ring went beyond my expectations. Stunning and perfectly crafted.
she said YES!
This ring looked even more stunning in person, just like my now-fiancée. She said YES, shed a few happy tears, and hasn’t stopped admiring it since. We couldn’t be happier. Thank you, GEMNAT! The resizing process was also effortless, thanks to the convenient online chat support.
I AM ALWAYS IMPRESSED!!
This is my third purchase from Gemnat and I’m still amazed 😍. Each piece is gorgeous, shipping is fast, and their customer service is super friendly. Definitely my go-to for jewelry now!
Big selection at great prices
This is actually my 2nd time buying a diamond ring online and I wish I knew about this site for my first one too! Tons of options and such good prices. Seriously, how do I give them 6 stars?
This bracelet is so nicely made, the detail is awsome!!
They helped me resize super easy!! fast and nice!!
They could not have been more helpful and professional and we were amazed with the service. Happy to recommend anyone who’s considering diamonds online
They are ABSOLUTELY TRUSTWORTHY!!!
These earrings are so simple but legit sparkle like crazy. Perfect for everyday or when I wanna look fancy. Website was smooth, shipped fast. Obsessed.
There customer service is very very patient when I had a problem with resizing. The ring that I order was a bit smaller but no need to worry since they had it resized for me. Everything was SMOOTH. Will definitely order from this shop again for sure.
The website is so user-friendly. You can easily access everything you want from rings, bracelets, pendants and earrings even wedding rings. They even sort out the colour of stones for buyers. All the designs are super nice it even makes me had a hard time to choose what to buy but I really wanted a tennis bracelet during that time but would probably buy a ring for my girl next time. They are highly recommended!! Customer service was nice because I have to make some adjustments with the chain length and they were patient on every process. Fast replies. Thank you, GEMNAT!!!
The ring is gorgeous, just like in the pictures. Totally in love with it. 😍
The ring is amazing and service is great.
The quality of this ring is incredible, especially for the price. It truly exceeded all my expectations.
Exactly as Expected
The product is Excellent. Exactly what we ordered and expected.
The person I gave these to loved them! They look really nice.
The perfect ring for my bride-to-be—unique, beautiful, and just like her. Gemnat made the whole process really smooth.
The jewelry is beautifully made, with rings available in an impressive range of sizes. Shipping is fast and always tracked for peace of mind. They offer a wide selection of pieces at very competitive prices. I’ll definitely be back for more amazing jewelry.
The craftsmanship on this sapphire ring is outstanding! Feels delicate yet strong.
The craftsmanship is first rate and the service is impeccable. And the best part is the prices. You can get great quality of diamonds in cheaper price than on other websites
Tanzanite just hits different. The diamonds enhance it beautifully. The website photos were accurate. Came well packaged and secure.
Superb Professional Service
Super service, extremely professional, very efficient, extremely responsive, and punctual.
Super pretty, exactly what I wanted. Fits perfectly!
Such a gorgeous ring. The stone isn’t too big or small, just perfect.
Such a brilliant experience here.
Stunning ring! The band is just the right width and goes perfectly with my Morganite solitaire (also from Gemnat). Really appreciated the smooth ordering process and excellent customer service.
So pretty, got compliments instantly
So far this experience has been great! The necklace is shiny and beautiful, and the packaging was lovely. ✨
So cute 😭
Sized perfectly, and all the diamonds are arranged so nicely. The glimmer is amazing. 💎
Simple, transparent, and secure website.
Simple design but diamonds catch the light beautifully. Feels like everyday luxury. Checkout smooth and secure. Delivery on time.
Simple and classy. I wear them with everything.
Amazing
Shipping was smooth, product amazing!!
She liked it!! Mission accomplished
Impeccable Craft
She cried OMG love love love!!
She LOVED the pendant and earrings! Totally worth it
SHE LOVES IT!! From the moment I popped the question, everyone has been complimenting the ring. Her birthstone and the personalized touch just make it perfect.
Ring fits perfectly.
Reliable. Excellent Service!
Really nice accent pieces.
Perfect gift, she loved it 💖
Perfect for everyday wear.
Outstanding customer service and experience. It is already our 2nd time buying a ring here and I always got what's expected. Very beautiful ring!!
Ordering was super easy. The shipping was fast, and the description was spot on. Very happy.