ENCYCLOPEDIA
Aquamarine Full Guide

Aquamarine, from the Latin aqua marina meaning “sea water,” is a pale blue to greenish-blue gemstone from the beryl family — the same group as emerald and morganite. Its serene color and exceptional clarity have made it a symbol of calm, youth, and lasting harmony. Historically believed to protect travelers and soothe emotions, aquamarine is the birthstone for March and is traditionally gifted for a 19th wedding anniversary
Characteristics of the Aquamarine
Etymology: From the Latin aqua marina, meaning "water of the sea".
Family: Beryl
Chemical Composition: Aluminum silicate with beryllium
Hardness: 7.5 to 8 on the Mohs scale
Density: 2.68 – 2.74
Optical Properties: Uniaxial birefringent
Refractive Index: 1.577 – 1.583
Birefringence: 0.004 – 0.008
Crystal System: Hexagonal

The origin of Aquamarines
Aquamarines deposits are numerous and have yet to run out of out of jewelry-grade raw material.
The most important deposits can be found in the following countries :
- Brazil
- Madagascar
- Nigeria
- Mozambique
High-quality deposits have recently been discovered in Pakistan and Afghanistan.
Carat
The carat is the standard unit of measurement for the weight of gemstones. One carat is equal to 200 milligrams (0.2 gram).
This should not be mistaken with karat, which is the indicator of purity for gold.
With their lower density, aquamarines will appear larger than other gemstones of similar cuts and weights, making them popular for larger pieces.
The color of the Aquamarine
The aquamarine's color ranges from light pastel blue to deeper blue. The intensity of the color will directly correlate with the presence of iron. Some aquamarines can also display greenish-blue hues.
The most sought-after aquamarines are the ones with deeper shades of blue, found in exceptional Brazilian aquamarines from the Minas Gerais region, in the Santa Maria de Itabira mine. The mine is nearly exhausted, making the extracted aquamarines very expensive.
Discover our Guide on the Colors of Gemstones.






The clarity of Aquamarines
Most aquamarines are free of inclusions visible to the naked eye, we call them "eye-clean". However with a loup or microscope, some inclusions can be detected, often in the shape of tubes, empty or filled with liquid.
This lack of inclusion allows the light to interact freely with the facets of the stone, making aquamarines a brilliant gemstone.
Cut & Shapes
The aquamarine, thanks to its lack of major inclusions can easily be cut into different shapes, depending on the rough material or the market demand. The most popular shapes however are the emerald cut, the round cut, oval and pear.
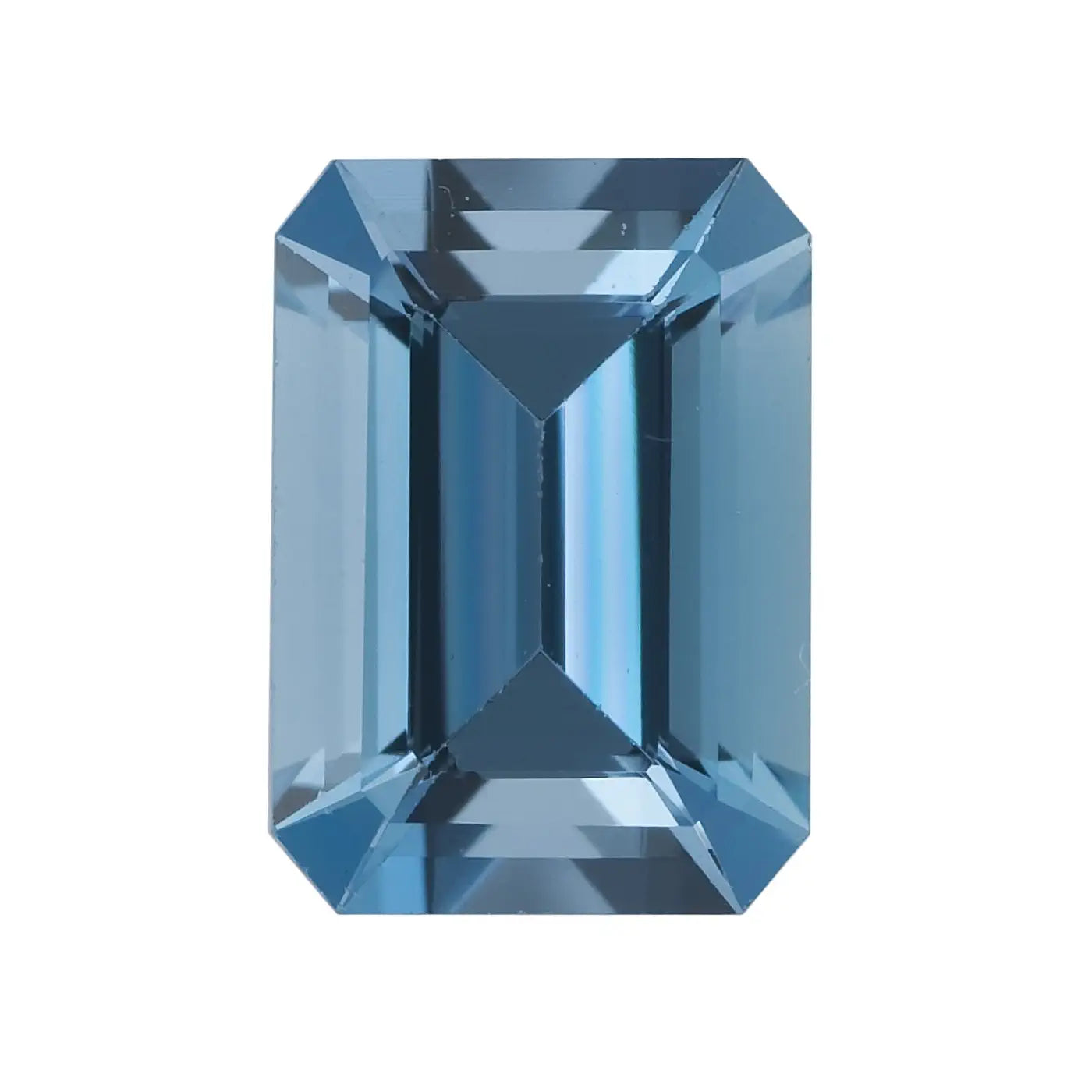
The emerald cut requires a deep enough color, as its step cuts increase the transparency of the stone. The higher count of facets on round, oval and pear aquamarine provide more sparkle and brilliance.

Round Shape Aquamarine

Oval Shape Aquamarine
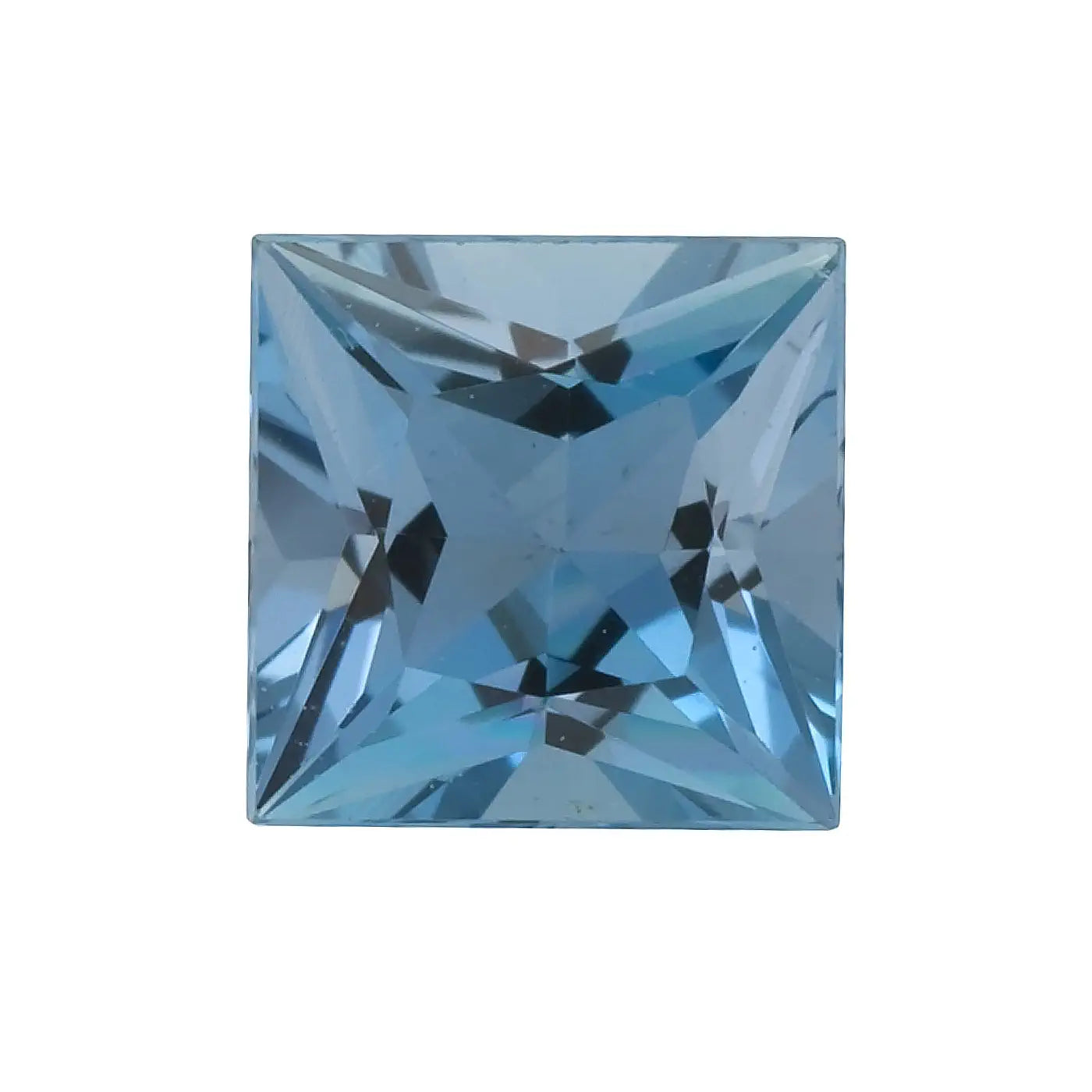

Princess Shape Aquamarine
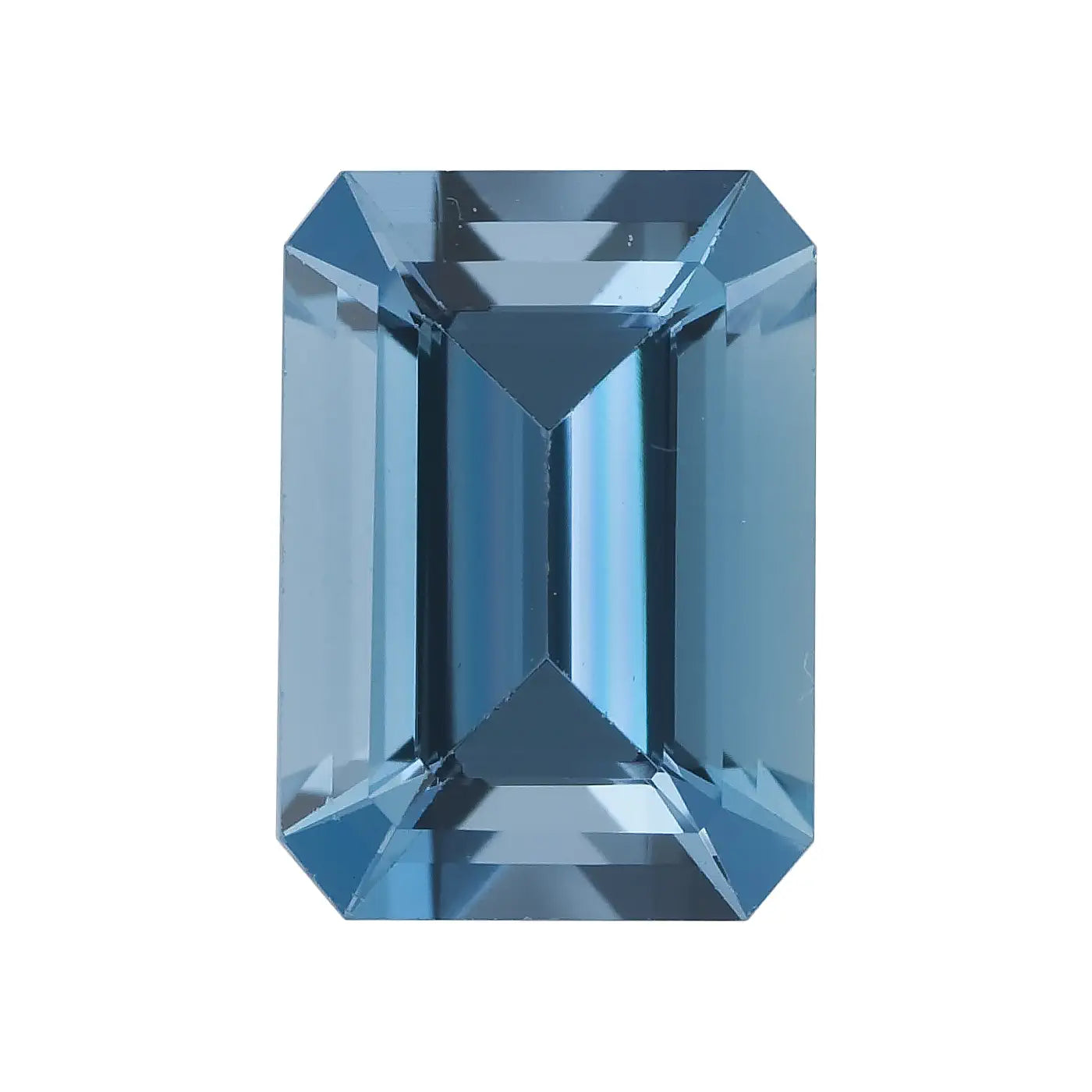

Emerald Cut Aquamarine

Pear Shape Aquamarine

Trillion Cut Aquamarine
Birthstone & Wedding Anniversary
The aquamarine is the birthstone for March.
It is also used to celebrate the 19th wedding anniversary in the United States.
Discover our Birthstone Full Guide.

Treatment
Most mined aquamarines contain green hues, which is sometimes even the main color. A controlled heat treatment will convert the ferric iron, which creates the green hue, to a ferrous iron to make the stone bluer.
Some stones, usually those lacking in color, may be irradiated, but the enhancement fades with time as it is exposed to light.
Unheated untreated aquamarines are extremely rare, thus making them highly valuable. You should always ask for a certificate from an independent laboratory to prove the stone has not been treated.
What Customers Are Saying
Superb Professional Service
Super service, extremely professional, very efficient, extremely responsive, and punctual.
Super pretty, exactly what I wanted. Fits perfectly!
Such a gorgeous ring. The stone isn’t too big or small, just perfect.
Such a brilliant experience here.
Stunning ring! The band is just the right width and goes perfectly with my Morganite solitaire (also from Gemnat). Really appreciated the smooth ordering process and excellent customer service.
So pretty, got compliments instantly
So far this experience has been great! The necklace is shiny and beautiful, and the packaging was lovely. ✨
So cute 😭
Sized perfectly, and all the diamonds are arranged so nicely. The glimmer is amazing. 💎
Simple, transparent, and secure website.
Simple design but diamonds catch the light beautifully. Feels like everyday luxury. Checkout smooth and secure. Delivery on time.
Simple and classy. I wear them with everything.
Amazing
Shipping was smooth, product amazing!!
She liked it!! Mission accomplished
Impeccable Craft
She cried OMG love love love!!
She LOVED the pendant and earrings! Totally worth it
SHE LOVES IT!! From the moment I popped the question, everyone has been complimenting the ring. Her birthstone and the personalized touch just make it perfect.
Ring fits perfectly.
Reliable. Excellent Service!
Really nice accent pieces.
Perfect gift, she loved it 💖
Perfect for everyday wear.
Outstanding customer service and experience. It is already our 2nd time buying a ring here and I always got what's expected. Very beautiful ring!!
Ordering was super easy. The shipping was fast, and the description was spot on. Very happy.
Customer Care + Craft = 💯
Ordered my fiancé’s engagement ring and there was a tiny issue with the addresses… I thought Christmas proposal was ruined 😭. But it showed up on Xmas Eve morning and I got to propose!! Super happy with the quality and how fast it got here.
Hassle-Free!!
Ordered a made-to-order amethyst bracelet for my mom. The stones are gorgeous and the design looks exactly like I imagined. There was a slight delay with shipping since I ordered it during Holiday season, but the team kept me updated the whole time. Mom was thrilled and I will definitely buy from them again!
GO FOR GEMNAT!!
Okay, jewelry addicts… the quality of these pieces is insane. Bought an eternity band elsewhere for double the price and it looked nothing like these. Gemnat has me hooked!!
OMG!!! MY GF CRIED WHEN SHE OPENED HER GIFT. BEST PURCHASE EVER
Love it
OMG this is literally PERFECT!! Exactly what I’ve been hunting for. It got to me crazy fast, the packaging looked super fancy, and ordering was a breeze. Customer service was super friendly too. Honestly, I’m blown away, can’t believe how smooth and amazing the whole experience was!
I have wanted a ruby since I was a little girl.
Now I finally have it and at 5cts this ruby is an absolute STUNNER!! I asked them to customize the design since I wanted a bigger stone than the 1ct they had on the page and they totally made it happen!! Had it set on a 1.5mm white gold box chain for extra strength and that perfect sparkly but classic vibe!! I’m SO in love with it!! Yay me!!!
Nice! Great quality, would definitely buy again.
My son gave this to his girlfriend and she was thrilled! It’s so dainty and gorgeous.
My new go to place when it comes to diamonds!
I'M OBSESSED!!!
My husband got it for my birthday and I am seriously obsessed!! The pink sapphire is so bright and sparkly, way prettier in person than I ever imagined. It fits perfectly and I get compliments on it literally every day!! I can’t stop staring at it, it’s just so gorgeous!!
My husband bought me this beautiful ring for our 10 years anniversary, absolutely stunning! Mine is 0.53 carat white gold and it goes well with my engagement and wedding ring together.
Absolutely Love My Ring!
My boyfriend bought me a ring from here, and I absolutely love it! It’s so beautiful and shiny. The quality is amazing. Totally recommend this place!
Mother’s Day ruby bracelet. On-time delivery, gorgeous, mom loved it. Highly recommended.
MY FAVEEE!
Made multiple purchases here and haven’t been disappointed yet! Tons of options for stone sizes and the quality is always on point.
Lovely pendant, perfect size. Bought it for my sister and she absolutely loved it!
Fantastic
Love the selection of gemstones, easy to pick the perfect one.
Love it!!!
OKAY I’M OBSESSED
Love it!! first jewelry purchase online and came flawless!!
So Classy!
Love it! Looks exactly like the pictures, great quality, and so elegant on the neck. Thank you for your professional service.
Love how it shines. Beautiful design and pairs perfectly with an engagement ring.
GREAT CHOICE!
Lots of choices to pick from and really worth the money
Looks better in person, wow ✨
Last minute gift panic but they helped me expedite!!
Prefect!
Just got my ring and I love it. The aquamarine is a really nice soft blue and the little diamonds on the side make it sparkle without being too much. Super happy with it exactly what I was hoping for.
I’ve had nothing but great experiences here. The quality of the jewellery is excellent
a 101% RECOMMENDED!!!
I’ve been planning to propose to my girlfriend for months, but I was terrified of choosing the wrong ring online 😅. I wanted something meaningful, unique, and perfect for her. She loves sapphires, so I started looking for one that would make her eyes light up. I stumbled upon Gemnat and honestly, I didn’t know what to expect. I ended up customizing a sapphire engagement ring with a slightly larger stone than the standard, and I kept imagining her reaction while biting my nails. When the ring arrived, I was blown away by how beautiful it was the stone sparkled like nothing I’ve ever seen, and the craftsmanship was impeccable. On the day I proposed, she literally gasped, had tears in her eyes, and said yes while covering her face. I’ve never seen her so happy, and the ring looked even more stunning on her than in the pictures. Gemnat made the whole process smooth, from customization to shipping, and even helped me with sizing questions. I can honestly say this was the most important purchase of my life, and it couldn’t have gone more perfectly. Thank you for making this moment unforgettable!