ENCYCLOPEDIA
Blue Sapphire Full Guide

Sapphire, from the Greek sappheiros, is a precious gemstone from the corundum family — which also includes ruby and pink sapphire. While best known in its deep royal blue, sapphire occurs in nearly every color except red. Renowned for its brilliance and hardness, it symbolizes loyalty, wisdom, and truth. As the birthstone for September, sapphire has long been associated with royalty and protection.
Unlike emerald, which belongs to the beryl family along with aquamarine and morganite, sapphire is exceptionally resistant — making it ideal for heirloom jewelry and daily wear.
Characteristics of the Blue Sapphire
Etymology: Derived from the Greek sappheiros, meaning a "blue gem".
Family: Corundum
Chemical Composition: Aluminum Oxide, with iron and titanium as color-inducing trace elements.
Hardness: 9 on the Mohs scale
Density: 3.95 - 4.03
Optical Properties: Uniaxial
Refractive Index: 1.762 - 1.770
Birefringence: 0.008 - 0.010
Crystal System: Trigonal / Hexagonal
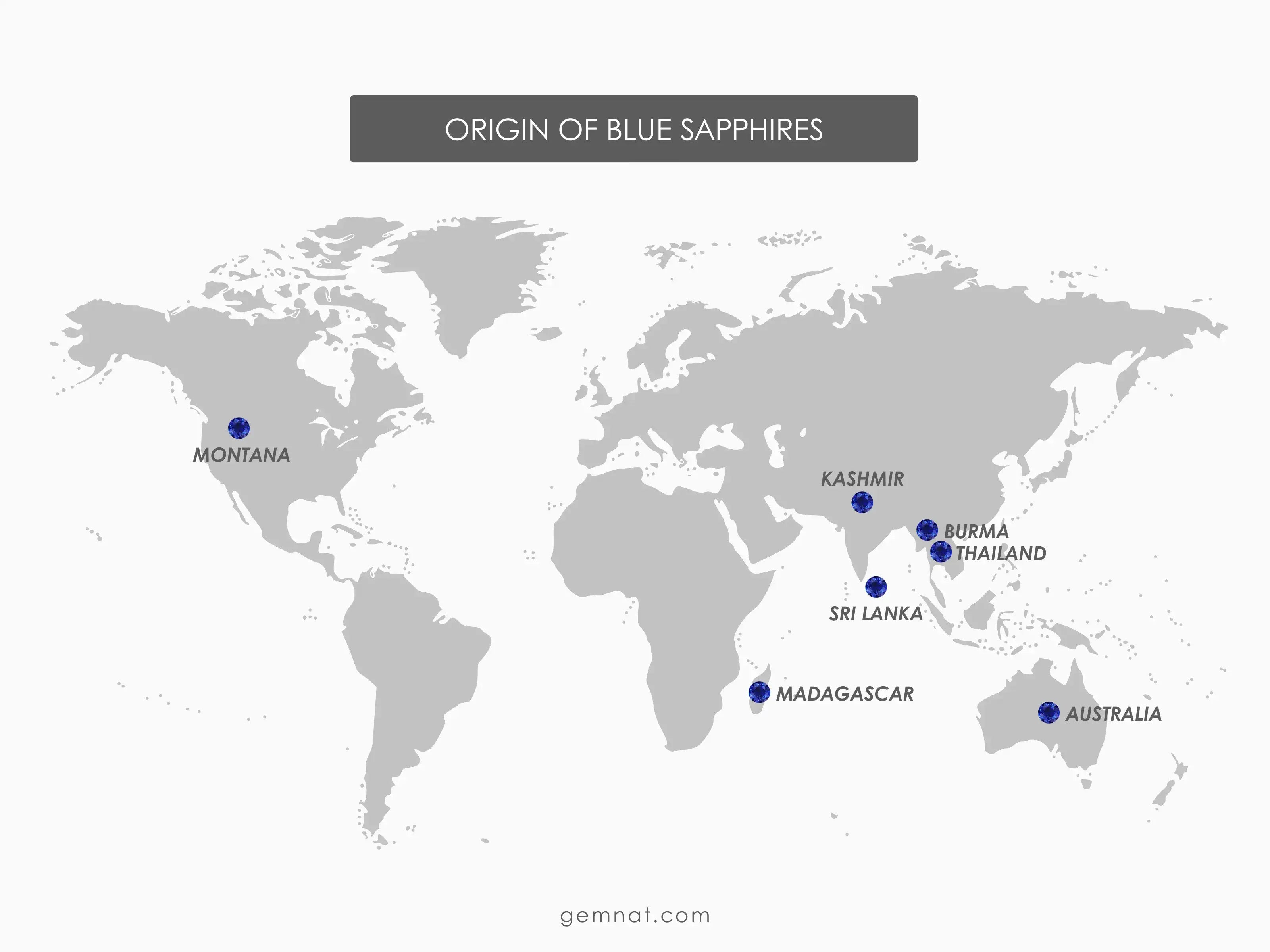
The origin of Blue Sapphires
The origin of blue sapphires is deeply connected to their geological formation, which occurs in certain types of metamorphic and igneous rocks under high temperature and pressure conditions deep within the Earth's crust. These conditions allow for the growth of corundum crystals, the mineral from which sapphires are formed. The blue color in sapphires is primarily due to the presence of trace amounts of elements such as iron and titanium.
Some of the most notable sources include:
- Sri Lanka
- Kashmir
- Thailand
- Madagascar
- Montana
- Australia
- Burma
Carat
The carat is the standard unit of measurement for the weight of gemstones. 1 carat equals 0.2 gram. For blue sapphires, the carat weight is a key factor in determining the gemstone's value.
It's important to distinguish between "carats," a measure of weight for gemstones like blue sapphires, and "karats," a unit indicating the purity of gold.
As sapphires are denser than most precious stones, a 1-carat round blue sapphire will be smaller than a 1-carat round diamond or 1-carat round emerald.
The color of Blue Sapphires
The color of blue sapphires is one of their most defining and valued characteristics. It ranges from pale, sky blue to deep, rich royal and navy blues. The most prized sapphires exhibit a vibrant, medium to deep cornflower blue, often referred to as "Ceylon Blue" after the traditional source in Sri Lanka.
The geographical origin of a blue sapphire can significantly influence its color. For instance:
Kashmir sapphires are renowned for their velvety, true blue color with a slight violet hue.
Sri Lankan (Ceylon) sapphires often have lighter, vibrant blues.
Burmese sapphires tend to display a deeper, intense blue.
Australian sapphires are known for darker hues, sometimes with a greenish tint.
Madagascar sapphires can vary widely, offering a range from pastel to rich royal blues.
Discover our Guide on the Colors of Gemstones.
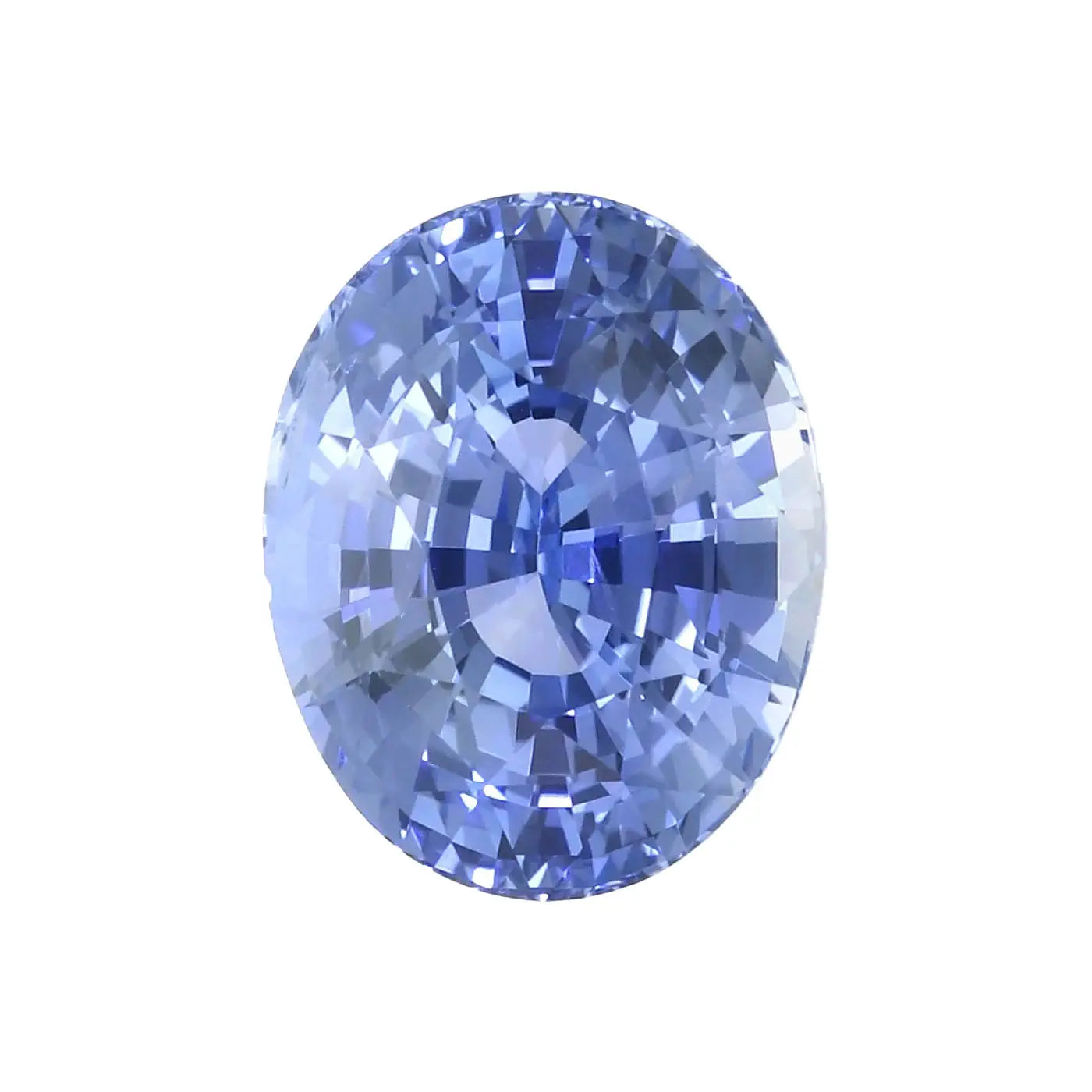

Cornflower blue sapphire
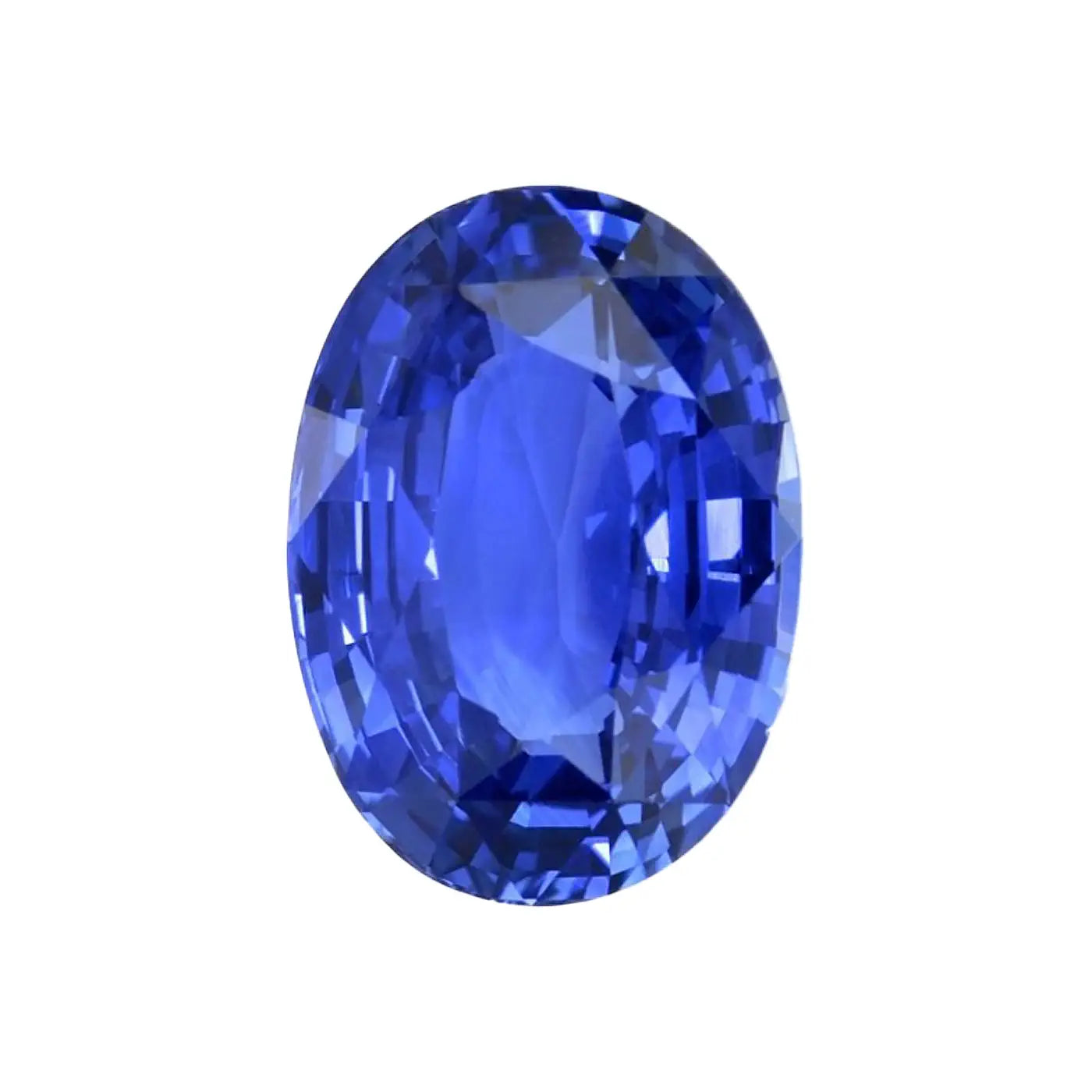

Ceylan blue sapphire
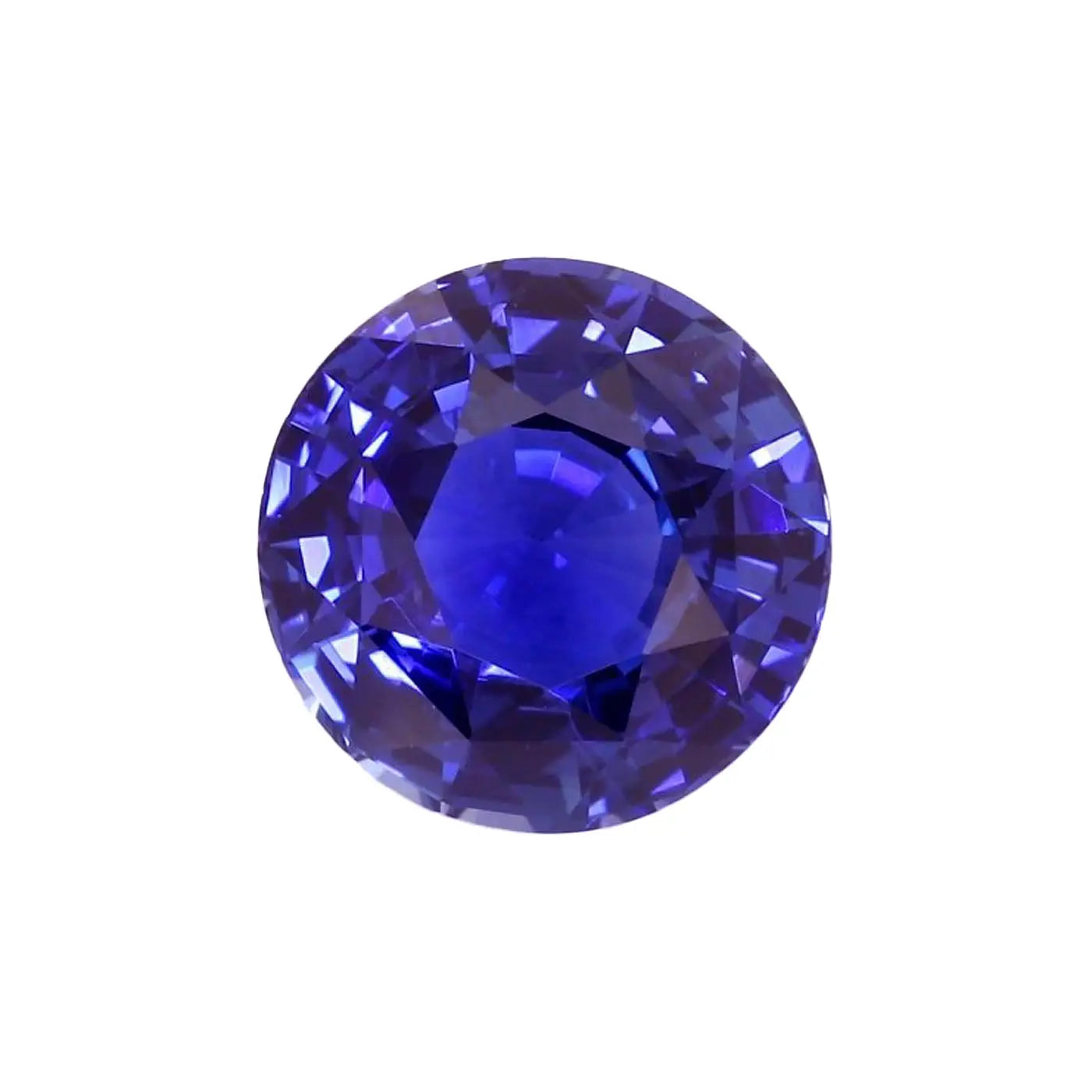

Purplish blue sapphire

Royal blue sapphire

The clarity of the Blue Sapphire
Clarity refers to the presence of internal features known as inclusions and external characteristics called blemishes. Clarity can significantly impact a sapphire's value, but it's important to note that because sapphires are colored gemstones, the clarity standards are not as stringent as those for diamonds.
In the case of cabochon sapphires, the inclusions can cause the apparition of a star under a specific light.
Cut & Shapes
Due to its hardness, the blue sapphire can be cut into many different shapes. The most common shapes for sapphires are the oval and the cushion cut as they limit the loss of raw material in the cutting process.
In order to bring out the best possible hue, the culet of the blue sapphires will often be deeper and slightly offset compared to diamonds of the same cut.

Blue Sapphire Round Shape

Blue Sapphire Emerald Cut
Blue Sapphire Princess Shape

Blue Sapphire Baguette Shape

Blue Sapphire Oval Shape

Blue Sapphire Marquise Shape
Birthstone & Wedding Anniversary
The blue sapphire is the birthstone for September.
It is also used to celebrate 16 years of marriage in France and 45 years of marriage in the United States.
Discover our Birthstone Full Guide.
Famous Blue Sapphires
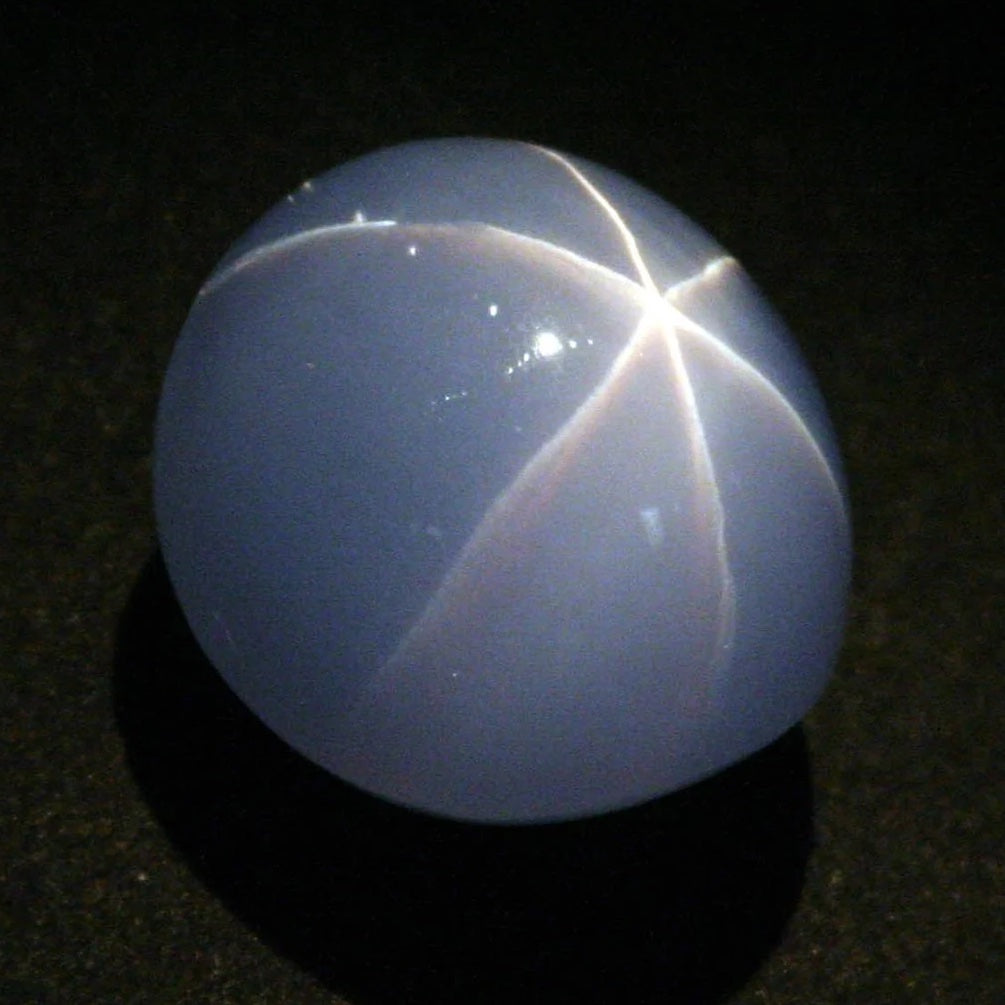

Star of India
One of the largest gem-quality blue star sapphires in the world, weighing 536 carats. Its unique feature is the star-like phenomenon known as asterism, visible on both sides of the stone due to its double cabochon cut. It is housed in the American Museum of Natural History in New York.
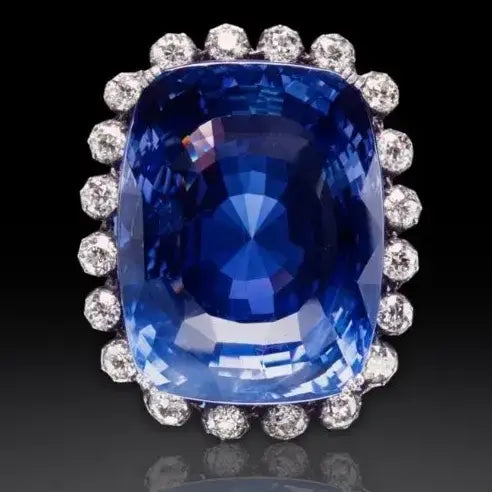

The Logan Sapphire
The Logan Sapphire, weighing approximately 423 carats, is one of the largest faceted Sri-Lankan blue sapphires and is known for its deep blue color. It is currently displayed at the National Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C.
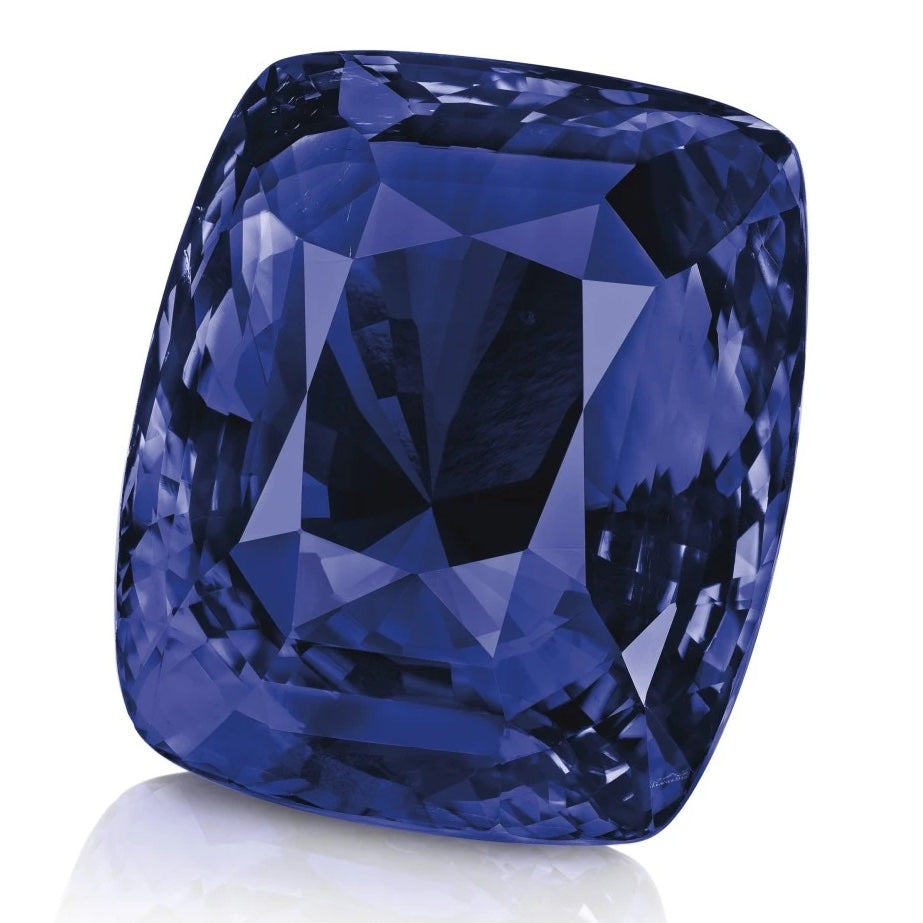

The Blue Belle of Asia
This 392-carat sapphire is one of the most famous sapphires in the world, known for its vibrant cornflower blue color. It was discovered in Sri Lanka in 1926 and has a storied history, including being auctioned for a record price at Christie's in Geneva.
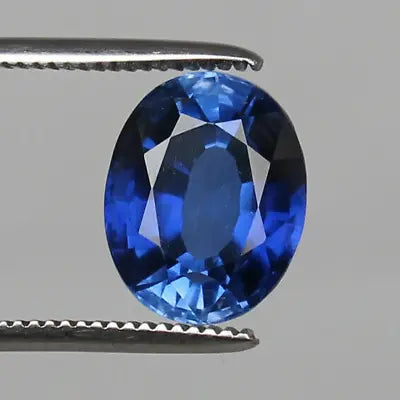

The Kashmir Sapphires
Sapphires from the Kashmir region are known for their exceptional quality and cornflower blue color. Although not a single stone, Kashmir sapphires in general hold a legendary status among gem enthusiasts.

Treatment
The most common treatment for blue sapphires is heat treatment, although other methods exist. Blue sapphires are often heated at temperatures between 1,500 and 1,800 degrees Celsius, to improve their clarity. Indeed, the heat helps crystallize the inclusions, making them less visible.
It is nowadays quite rare to find unheated sapphires of satisfying color, which makes them even more valuable.
What Customers Are Saying
Tanzanite just hits different. The diamonds enhance it beautifully. The website photos were accurate. Came well packaged and secure.
Superb Professional Service
Super service, extremely professional, very efficient, extremely responsive, and punctual.
Super pretty, exactly what I wanted. Fits perfectly!
Such a gorgeous ring. The stone isn’t too big or small, just perfect.
Such a brilliant experience here.
Stunning ring! The band is just the right width and goes perfectly with my Morganite solitaire (also from Gemnat). Really appreciated the smooth ordering process and excellent customer service.
So pretty, got compliments instantly
So far this experience has been great! The necklace is shiny and beautiful, and the packaging was lovely. ✨
So cute 😭
Sized perfectly, and all the diamonds are arranged so nicely. The glimmer is amazing. 💎
Simple, transparent, and secure website.
Simple design but diamonds catch the light beautifully. Feels like everyday luxury. Checkout smooth and secure. Delivery on time.
Simple and classy. I wear them with everything.
Amazing
Shipping was smooth, product amazing!!
She liked it!! Mission accomplished
Impeccable Craft
She cried OMG love love love!!
She LOVED the pendant and earrings! Totally worth it
SHE LOVES IT!! From the moment I popped the question, everyone has been complimenting the ring. Her birthstone and the personalized touch just make it perfect.
Ring fits perfectly.
Reliable. Excellent Service!
Really nice accent pieces.
Perfect gift, she loved it 💖
Perfect for everyday wear.
Outstanding customer service and experience. It is already our 2nd time buying a ring here and I always got what's expected. Very beautiful ring!!
Ordering was super easy. The shipping was fast, and the description was spot on. Very happy.
Customer Care + Craft = 💯
Ordered my fiancé’s engagement ring and there was a tiny issue with the addresses… I thought Christmas proposal was ruined 😭. But it showed up on Xmas Eve morning and I got to propose!! Super happy with the quality and how fast it got here.
Hassle-Free!!
Ordered a made-to-order amethyst bracelet for my mom. The stones are gorgeous and the design looks exactly like I imagined. There was a slight delay with shipping since I ordered it during Holiday season, but the team kept me updated the whole time. Mom was thrilled and I will definitely buy from them again!
GO FOR GEMNAT!!
Okay, jewelry addicts… the quality of these pieces is insane. Bought an eternity band elsewhere for double the price and it looked nothing like these. Gemnat has me hooked!!
OMG!!! MY GF CRIED WHEN SHE OPENED HER GIFT. BEST PURCHASE EVER
Love it
OMG this is literally PERFECT!! Exactly what I’ve been hunting for. It got to me crazy fast, the packaging looked super fancy, and ordering was a breeze. Customer service was super friendly too. Honestly, I’m blown away, can’t believe how smooth and amazing the whole experience was!
I have wanted a ruby since I was a little girl.
Now I finally have it and at 5cts this ruby is an absolute STUNNER!! I asked them to customize the design since I wanted a bigger stone than the 1ct they had on the page and they totally made it happen!! Had it set on a 1.5mm white gold box chain for extra strength and that perfect sparkly but classic vibe!! I’m SO in love with it!! Yay me!!!
Nice! Great quality, would definitely buy again.
My son gave this to his girlfriend and she was thrilled! It’s so dainty and gorgeous.
My new go to place when it comes to diamonds!
I'M OBSESSED!!!
My husband got it for my birthday and I am seriously obsessed!! The pink sapphire is so bright and sparkly, way prettier in person than I ever imagined. It fits perfectly and I get compliments on it literally every day!! I can’t stop staring at it, it’s just so gorgeous!!
My husband bought me this beautiful ring for our 10 years anniversary, absolutely stunning! Mine is 0.53 carat white gold and it goes well with my engagement and wedding ring together.
Absolutely Love My Ring!
My boyfriend bought me a ring from here, and I absolutely love it! It’s so beautiful and shiny. The quality is amazing. Totally recommend this place!
Mother’s Day ruby bracelet. On-time delivery, gorgeous, mom loved it. Highly recommended.
MY FAVEEE!
Made multiple purchases here and haven’t been disappointed yet! Tons of options for stone sizes and the quality is always on point.
Lovely pendant, perfect size. Bought it for my sister and she absolutely loved it!
Fantastic
Love the selection of gemstones, easy to pick the perfect one.
Love it!!!
OKAY I’M OBSESSED
Love it!! first jewelry purchase online and came flawless!!
So Classy!
Love it! Looks exactly like the pictures, great quality, and so elegant on the neck. Thank you for your professional service.
Love how it shines. Beautiful design and pairs perfectly with an engagement ring.
GREAT CHOICE!
Lots of choices to pick from and really worth the money
Looks better in person, wow ✨
Last minute gift panic but they helped me expedite!!
Prefect!
Just got my ring and I love it. The aquamarine is a really nice soft blue and the little diamonds on the side make it sparkle without being too much. Super happy with it exactly what I was hoping for.
I’ve had nothing but great experiences here. The quality of the jewellery is excellent